Detect & Fix Crashes in Android Apps | Appxiom
Detect crashes in Android apps in real-time. Appxiom helps teams identify root causes and fix crashes faster.
Crashes in Android Applications
What are Crashes in Android apps?
A crash in Android applications refers to the sudden and unexpected termination of an app while it is running. This can happen due to various reasons such as programming errors, memory leaks, insufficient device resources, or compatibility issues.
When an app crashes, the user is usually presented with a message that informs them of the app's termination. The message may provide the user with the option to either force stop the app or send a crash report to the app's developer. A crash report usually contains information about the events leading up to the crash, such as the device's state, the app's logs, and any error messages that were generated.
Crashes can be frustrating for both users and developers. For users, crashes can lead to data loss, device instability, and a poor user experience. For developers, crashes can lead to negative reviews, lost revenue, and a damaged reputation.
Therefore, it's crucial for developers to monitor their apps' performance and identify any potential issues that could lead to crashes. This can be done by conducting regular testing, optimizing the app's code and resources, and implementing crash reporting tools to quickly identify and resolve any issues that arise.
Reasons for Crashes in Android apps
Crashes in Android applications can occur due to various reasons, some of which are:
Memory leaks:
Memory leaks can occur when an app fails to release memory it no longer needs, causing the app to consume more and more memory until it crashes.
NullPointerExceptions (NPEs):
NPEs occur when an app tries to access an object that is null or doesn't exist, resulting in a crash.
OutOfMemoryError:
This occurs when an app tries to allocate more memory than is available, causing the app to crash.
StackOverflowError:
This occurs when an app's call stack becomes too large, often caused by infinite recursion or a function calling itself too many times.
Incompatible device:
Sometimes an app can crash because its features are not compatible with a particular device or set of devices.
User input errors:
If an app doesn't handle user input correctly, it may cause the app to crash.
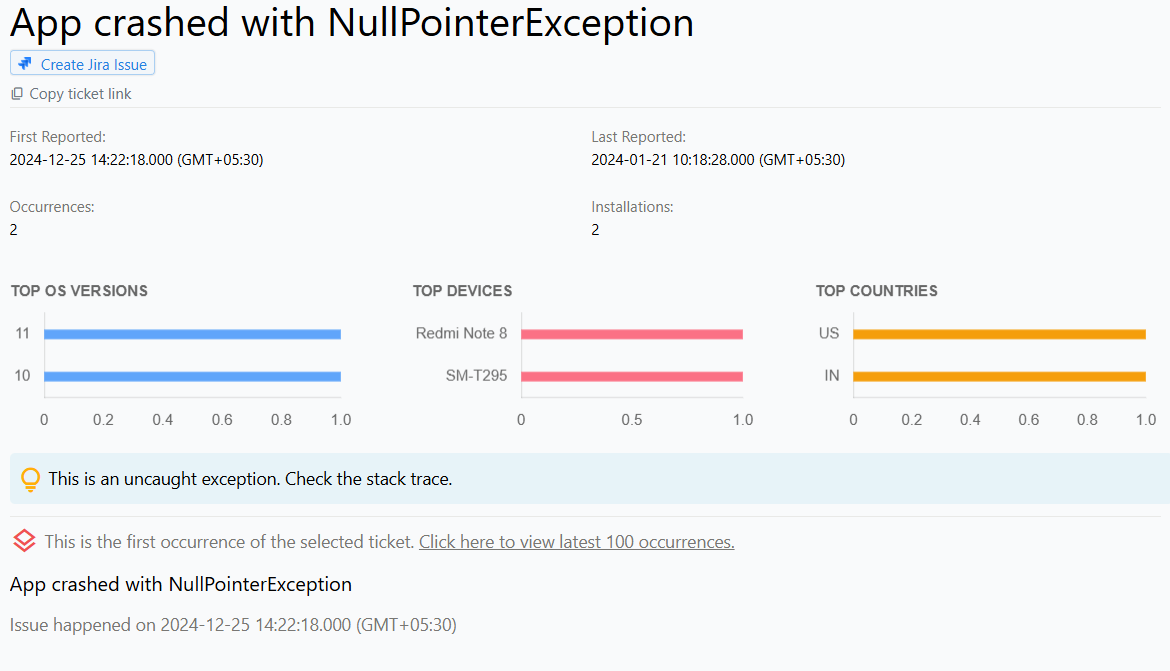
How do we use the information in the screenshot to fix Crashes in Android apps?
An issue report for a crash in Android applications typically includes the name and reason for the crash, as well as a stack trace. The stack trace can help developers identify the root cause of the issue.
In addition, the crash report often includes an activity trail, which is a chronologically ordered list of events that occurred prior to the crash. This can provide helpful context for understanding the circumstances that led to the crash.